The RRS met for our monthly meeting on Friday, October 12, 2018, at the Ken Nakaoka Community Center in Gardena. As usual, we got started by calling the meeting to order and reading the treasury report. We had a big agenda but covered most of the topics.
[X1]
Richard Garcia wasn’t able to join us at the October meeting. He wanted to report that he has made some design improvements to the RRS standard liquid rocket. He’s finished upgrading his engine design code to be able to analyze a blowdown engine (pressure-fed from the tanks). He also will soon have drawings for a thrust chamber design.
With some luck, I hope he’ll be back into testing at the MTA sometime soon next year.
[X2]
Electro Tech Machining (ETM) in Long Beach, California, specializes in graphite stock, graphite parts and Electrical Discharge Machining (EDM). They are experts and have been a loyal supporter of amateur rocketry groups such as UCLA and USC. The Reaction Research Society is happy to endorse them as they have been a great support to our society member’s projects as well.

Electro Tech Machining – Long Beach, contact information
Contact Cathy Braunsdorf at Electro Tech Machining.
Electro Tech Machining
2000 W. Gaylord Avenue
Long Beach, CA, 90813
(562) 436-9281
Electro Tech Machining in Long Beach, the graphite specialists
Electrical Discharge Machining (EDM) – Wikipedia article
I stopped in this week to pick up some round stock for making more graphite nozzle pucks for the ballastic evaluation motor (BEM) that is nearing completion. Graphite makes an excellent high temperature material for nozzle throats or any low ablation surfaces. We have used graphite inserts into reclaimed alpha and beta nozzles over the years at the RRS. Our society members have used graphite throats in their larger solid motor tested at the RRS MTA back in June 2018.

Plastic nozzle puck used for scale against the graphite round stock acquired by the RRS from Electro Tech Machining in Long Beach, CA
Moving into the meeting agenda, we shifted the order a little, but I have kept the numbering the same:
[1]
The latest educational event at Weigand Elementary school in Watts is going very well. The LAPD CSP program continues to help sponsor the event and we get great excitement from the kids. This Friday was the fifth of six educational events where they get to assemble the empty rockets. Osvaldo, Larry and Frank were on hand to help with the build process. The kids are really enjoying the process of learning and painting the team rockets will done in the last session before going out to launch at the RRS’s private testing site, the Mojave Test Area (MTA).

Two of our young participants show their assembled RRS alpha rocket at Weigand Elementary, Frank Miuccio in the background at the right
[2]
The next launch event at the RRS MTA will be the final step in the RRS’s educational program for Weigand Elementary school. We have this scheduled for October 27th and we hope to have cooler weather than in prior events now that the summer has passed. We have nine alphas from Weigand Elementary and three more alphas from our new membership, Wilbur Owens, Xavier Marshall and Michael Lunny.

Xavier Marshall looks over his first RRS alpha, welcome to the club!
[3]
I gave my quarterly briefing on the SuperDosa project at the October meeting. This time, I organized my thoughts and ideas into a presentation to give the RRS a general overview of the project and where we are so far.
Largely, I wanted to reiterate the project’s overall goals to many of the new members who have joined the RRS since the project’s inception in January 2017. The RRS intends to retake the amateur rocketry altitude record and in the process reopen our ability to make larger solid rocket motors and expand our reach both in our own community and literally with payloads ultimately flying above the atmosphere.

SuperDosa quarterly report, Oct-2018
I also acknowledged the recent progress of some of our new members formerly of the Chaminade Rocketry Club. Also, USC had a launch attempt with their Traveller III rocket, part of their Spaceshot Initiative. Unfortunately, instrumentation was not functioning but the flight looked to be nearly perfect. I hope USC will come present their recent accomplishments at a future RRS meeting.
Materials acquisition and some discussion about how to proceed with the propellant burn rate testing were the highlights of the discussion. More progress needs to be made in a few areas for completing the first prototype:
(a) Complete the design of all parts for the first prototype (6-inch booster)
(b) Begin prototyping instrumented dart payloads to practice flying and recovering these while getting good data. Making these devices work under the tight and unforgiving conditions that they must.
(c) More work in parachute recovery
(d) Estimating friction heat loads and heat mitigation strategies for the payload
Much of this prototyping work can be done at the MTA by flying smaller subscale vehicles and testing subsystems to prove they can work. More importantly, these tests give the society practice for the large vehicle testing which will reclaim the altitude record for the RRS.
The response to the SuperDosa project’s progress was very constructive and many new ideas were offered. I’m thankful to Frank, Steve Majdali, Larry, Osvaldo, Bill Behenna, Drew and Xavier for their inputs. I have taken notes and given actions to other members who are willing to help advance key areas of the project. Unfortunately, this topic was to be the last of the evening as my presentation easily exceeded the 20 minutes I intended.
The next quarterly report for the SuperDosa project will be January 11, 2019, and I hope to report a great deal of progress.
[4]
We had a last minute addition to the agenda, with Steve Majdali talking about black powder rockets and some very nice black powder rocket making tools he acquired while on travel. Black powder rockets are a classic form of amateur rocketry and involve many techniques that are broadly useful in other areas such as composite grain motors.

Steve Majdali shows the RRS his metal spindle for a cored grain type of 3-inch black powder rocket
Steve gave us a lot of great information specific to black powder making, pressing and a wealth of other practical information. Based on this new avenue of research, I felt the RRS would benefit more if Steve discussed this topic in more length in a stand-alone article soon to be published here on the RRS.ORG website.
[5]
The RRS has been in contact with the Additive Rocket Corporation (ARC) of San Diego. They are a startup company in San Diego with the goal of making high performance rocket motors using their novel design methodologies and 3D metal printing equipment. Discussions are still underway and thus there wasn’t much to tell. ARC was an exhibitor at the 75th anniversary symposium this year in April.

Additive Rocket Corporation (ARC) of San Diego at the 75th anniversary RRS symposium
[6]
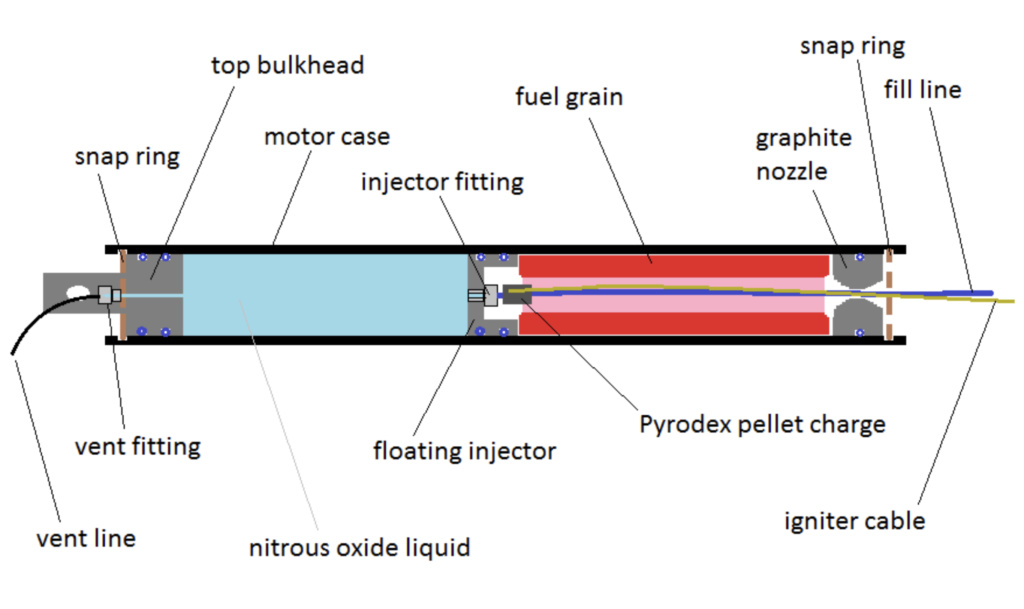
In my discussions with ARC, they were kind enough to offer to 3D print a simple small liquid rocket chamber I designed. Prices are not cheap, but this futuristic manufacturing technique offers a great deal of complexity that is not easily nor cheaply replicated by traditional means. I have been in discussions with ARC and hope to have more to present at the next RRS meeting.

125 lbf thrust chamber design, uncooled; prototype for the RRS standard liquid project
[7]
Alastair Martin could not join us at October’s meeting. I was going to have him discuss the current topics of interest at the recent 21st Annual Mars Society Convention held this summer. Alastair is very involved with the Mars Society and the RRS.

Alastair will be at the November RRS meeting so we’ll put this topic on the next agenda.
[8]
New RRS members, Wilbur Owens and Xavier Marshall, are active with the Experimental Aircraft Association, chapter #96, at the Compton Airport in the Los Angeles area. EAA-96 is a like-minded group of enthusiasts centered on experimental aircraft. The EAA-96 has hangar space and a range of machining tools offered to their members.
Experimental Aircraft Association, Spirit of 96
Xavier had mentioned at the last meeting that the EAA would love to host a visit by the RRS. Accepting the EAA’s invitation, the RRS has scheduled a visit to the EAA in Compton on November 3rd at 10:00AM. The EAA will give an hour tour of their facilities and projects. We hope to foster a strong relationship between the EAA and the RRS.
Talk with Xavier Marshall, Wilbur Owens, the RRS president, vice president or secretary for details.
Experimental Aircraft Association (EAA) hangar
1017 W. Alondra Blvd.
Compton, CA, 90220
(310) 612-2751
One of the key points of discussion at this visit will be to discuss how the RRS and EAA can help each other or participant in joint projects. The RRS is interested in using the EAA hangar facilities if they are available. Annual membership at the EAA is $40 to the EAA national society and $40 more to the local chapter at the Compton Airport. As I understand but must confirm, with EAA-96 chapter membership, RRS membership can have access to the machining tools for building rocketry parts for those of us without facilities in our own homes.
Xavier had also mentioned that hangar storage was often very cost-effective which could be a service that the RRS could use as we look to expand our shop capabilities to our membership.

EAA Chapter 96 hangar, Compton Airport
The EAA hangar is just straight east and not very far from our regular meeting location in Gardena at the Ken Nakaoka Community Center just north of Artesia Blvd. (CA-Hwy 91). The address is above.
[9]
Osvaldo’s recent successful design of an alpha parachute recovery system was not able to be covered. We may expand this topic into a fully illustrated RRS.ORG article if we can not get this topic on next month’s agenda. This has been a quiet success and definitely worthy of exhibition to our membership.
[10]
Jerry Fuller of Aerospace Corporation had indicated interest in building and testing a larger subscale prototype of his liquid-infused hybrid motor grain. Aerospace had earlier this year successfully demonstrated a smaller prototype in flight at the RRS MTA. In choosing the next larger design, he has selected a common model rocketry size (98 mm) just under 4-inches which will allow him to use commercially available rocket body parts. Jerry is active with our friends at Rocketry Organization of California (ROC).

At this time, he is still working on the design until resources can be allocated. The RRS has invited him to present his results and the new prototype he has in mind. The RRS is happy to support private groups with a testing area and a community of amateur enthusiasts happy to assist.
[11]
The RRS had discussed having a small group of our membership go out to the next ROC event which is held the 2nd Saturday of the month. Unfortunately, neither I nor Drew were able to go this month. With the Friday night rains falling on the city, it might not bode well for the event at the Lucerne Valley as they must operate on the dry lake bed.
We are looking to coming out to the November ROC event in the Lucerne Valley and hope we can bring other RRS memmbers with us. In particular, some of our members are interested in getting more practical experience through the NAR or Tripoli prefect at ROC. Moreover, some of the RRS membership is seeking experience and support as we acquire letters of recommendation for the California pyro-op licensing in rocketry.
[12]
Saturday seminars have not yet been scheduled, but the RRS is still committed to offering an extended time period for fuller discussions by invited speakers.
[+] RRS member, Jim French, is a speaker of which we would be very excited to have. Jim was a development engineer at the famed Santa Susanna Field Laboratory here in Los Angeles during the development of the reliable and powerful H-1 engine and the injector for the massive F-1 engine. Later, he worked at TRW on the reliable, hypergolic fueled, Apollo Descent engine at TRW at their San Juan Capistrano testing site (now defunct). His book, “Firing a Rocket Engine” is available on Amazon and it is a great read.
Amazon.com – James A. French, Firing a Rocket Engine
[+] Reaction Research Society founder, George James, is another speaker we have been wanting to have. His founding work with his other organization, the Rocket Research Institute (RRI) was a great topic he covered only briefly at the 75th anniversary symposium in April.
[+] Rocketdyne retiree and materials expert, John Halczuk, is another potential speaker on the subject of his extensive research of the V-2 rocket. He gave an excellent talk last year at California State University in Northridge, on history of the V-2’s development and deployment. The V-2 guided many design decisions still used in modern rocketry today in both the United States and particularly in the former Soviet Union.
We were not able to discuss this topic in detail, but more information will be forthcoming, hopefully in the form of an announcement of our first Saturday seminar at the Ken Nakaoka Community Center on a Saturday morning.
[13]
The next RRS symposium date in 2019 will be set soon. Based on the powerful success of the 2018 event, the RRS has decided to further the tradition one more year. We hope to have an even better mixture of universities, private companies and government agencies.

Date to be announced in November, the RRS will hold the 2019 symposium at the Ken Nakaoka Community Center in Gardena
There was no time to formally raise the subject, but it was decided by the council members present at the October meeting that the 2019 RRS symposium date will be formally set by an offline discussion and the date officially announced at the next RRS meeting on November 9, 2018.
[IN CLOSING]
The next meeting of the RRS will be November 9th at the Ken Nakaoka Community Center in Gardena.
We will most certainly discuss the results of the MTA launch event scheduled for Saturday, October 27, 2018. I will build the agenda starting at the end of the month. Please contact the RRS secretary for ideas and information on meeting topics.
secretary@rrs.org
As per our constitution, the RRS will hold its annual nominations of officers for the next calendar year 2019 at the November 9, 2018 meeting. Voting by the administrative membership will take place thereafter and managed by our election chairman. Results will be announced at the next meeting on December 14, 2018.
Thank you for reading.
—- —-